Service hotline
Support and counselling via: Tel: +49(0)89-1890846-0
Mo to Th from 09:00 to 17:00
Fr from 09:00 to 15:00
Or via our contact form.
What does does osmosis and reverse osmosis exactly mean?
Osmosis refers to the flow of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane in order to achieve a balanced ion concentration. Osmosis is an important process for the regulation of the fluid balance of cells and living beings. Virtually all metabolic processes function according to the principle of natural osmosis. If two liquids of the same type are separated by this membrane, there is no difference in pressure and the liquid molecules can move freely through the membrane without having to create a balance in pressure. If, however, there is pure water on one side and a saline solution on the other - the salt leaves less space for the water molecules - the water molecules of the distilled side would migrate to the saline resp. contaminated side until the number of molecule exchange on the two sides is equalized, thus increasing the pressure on the contaminated liquid side.
In reverse osmosis, a pressure-generating pump presses contaminated water against a filter material (semi-permeable membrane) in such a way that the contaminants in the water stick to the membrane, thus filtering and cleaning the water molecules. Without this artificially generated pressure, the water molecules would flow back to the contaminated side for reasons of chemical balance.
How does reverse osmosis work?
In order to obtain water that is as pure and filtered as possible, a counter pressure is generated on the contaminated side of the liquid, e.g. tap water, that is significantly higher than the osmotic pressure and prevents the water molecules from flowing back into the contaminated side. The osmosis principle is now reversed and what we call reverse osmosis is created.
In a reverse osmosis system, the polluted water is drained off along the membrane so that the filter material does not get clogged and a certain amount of concentrate can be adjusted, for example to prevent lime precipitation in the membrane. The concentrate then contains the polluted substances of the contaminated water (e.g. tap water), these are drained off. The outcome is purified and healthy water free of pollution.
To our reverse osmosis plants:
A comparison of different drinking water filter systems (German version)
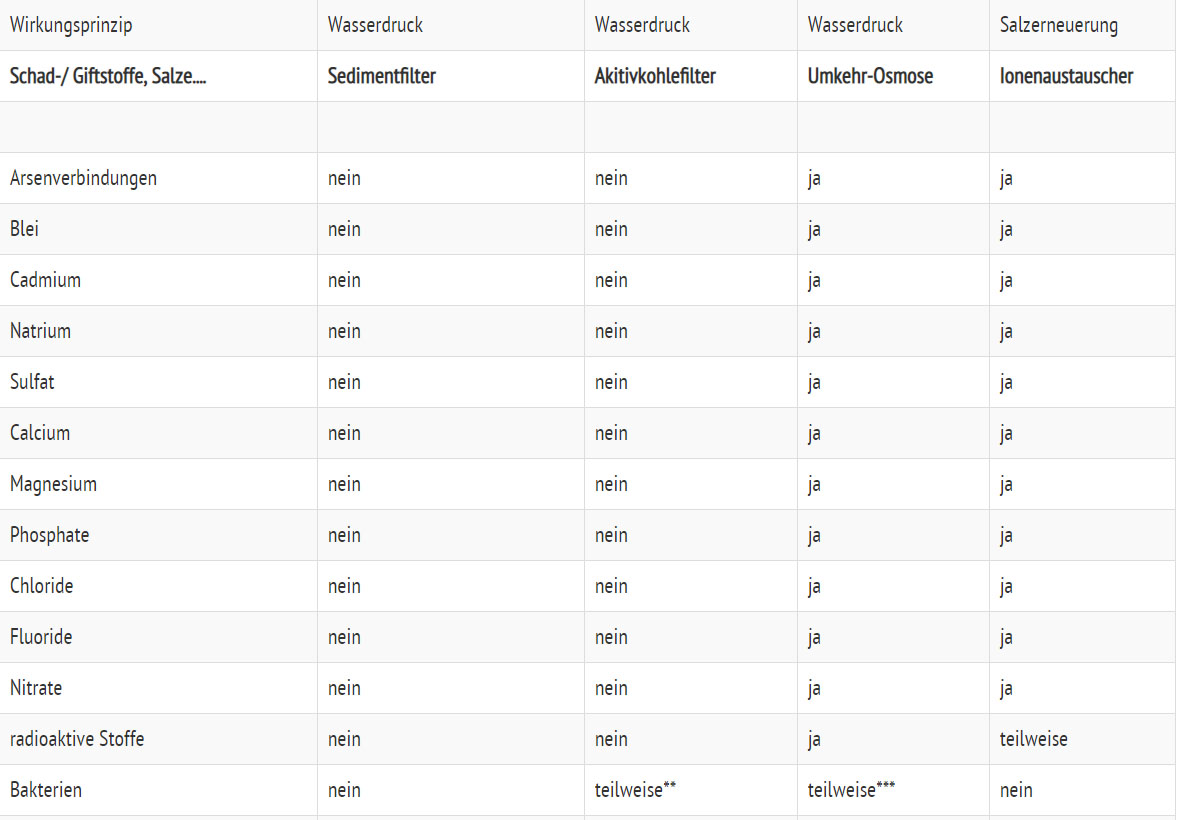
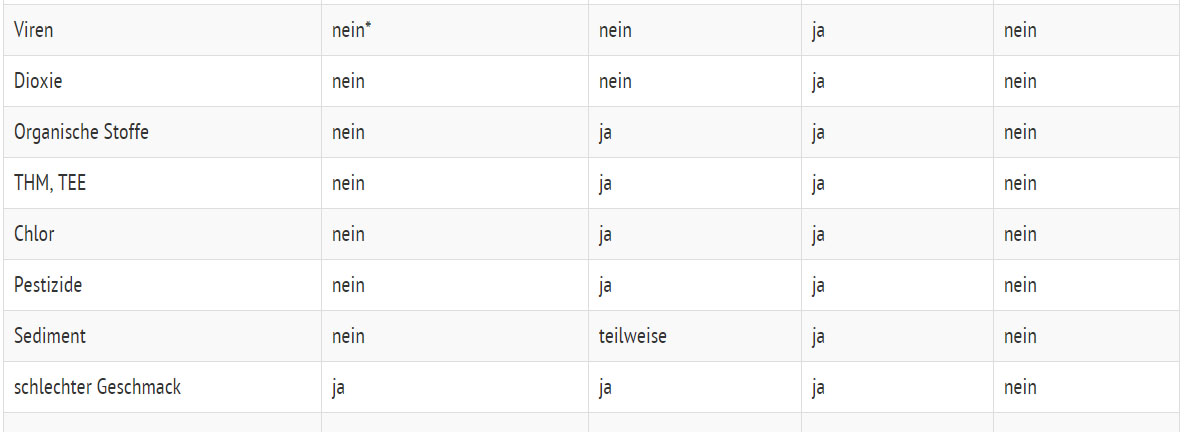
no = no distance, partial = partial distance, yes = distance
* Ceramic filters are suitable
** When activated carbon is coated with silver ions
*** Tap water contaminated with pathogenic germs is extremely rare. In the case of contaminated well water, all manufacturers recommend a UV disinfection lamp or other suitable desinfection methods, as living bacteria can, in the worst case, settle down on or grow through the membrane, if a system has not been in use for a long time.
